Toward the 30 by 30 goal. What is the difference between an OECM and a natural symbiosis site?
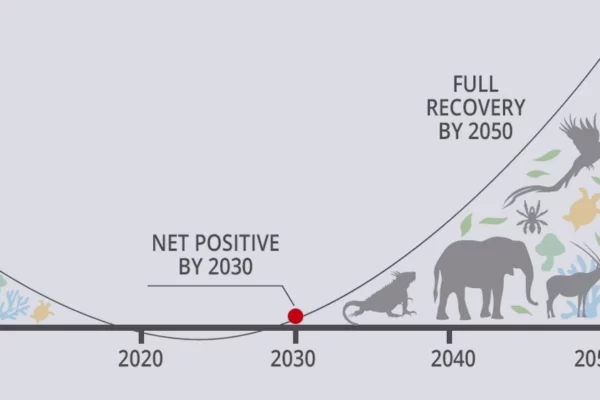
The “30 by 30” goal, which became an international commitment at the G7 Summit in 2021 along with Nature Positive, is to target 30% each of land and sea for conservation by 2030.
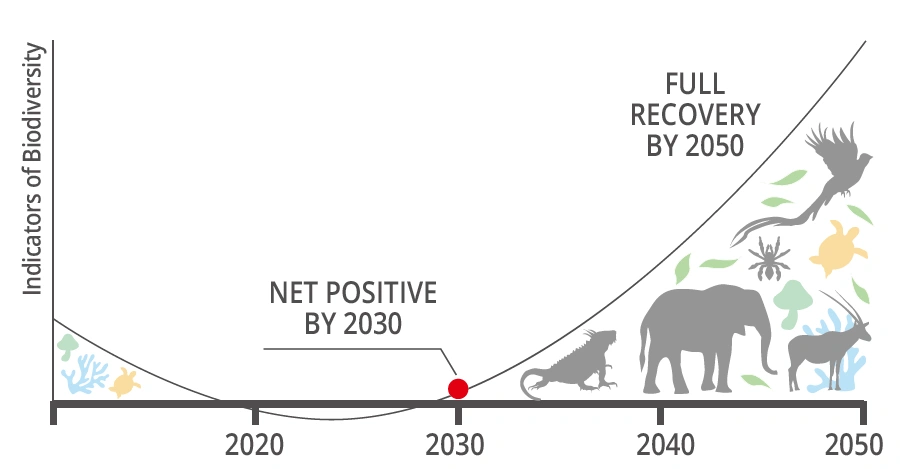
While national parks and other Protected Areas (PAs) can be strongly enforced to conserve the natural environment, they are difficult to expand, making it difficult to achieve the 30% target.
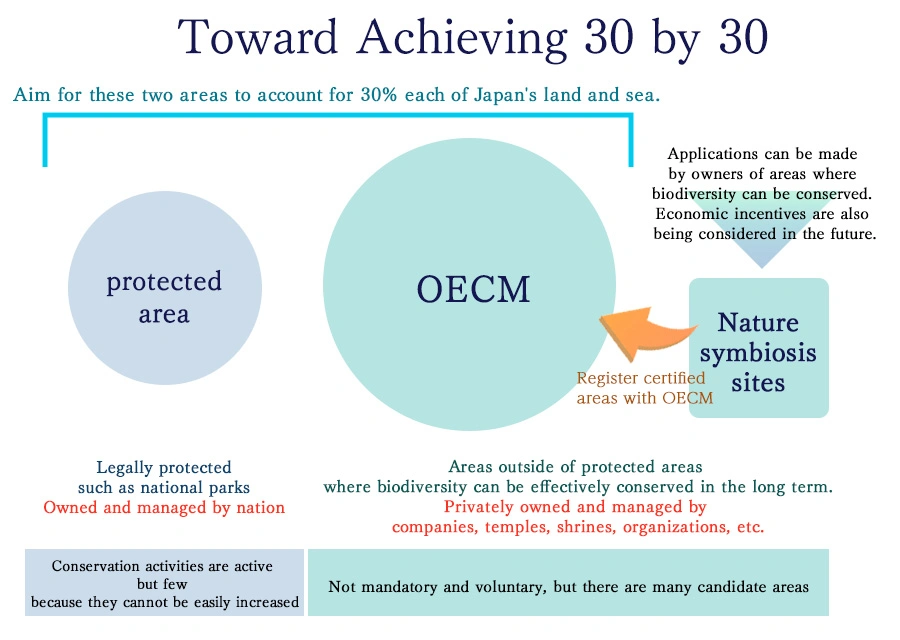
Therefore, efforts are underway to certify areas other than legally protected areas such as national parks that contribute to environmental conservation and biodiversity maintenance as Other Effective Area-based Conservation Measures (OECMs) , and to conserve and monitor these areas.
As for the status of achievement by other countries, Germany is the only country that has exceeded 30% of both land and sea PAs alone*1.
The situation differs from country to country, but many countries seem to have a policy of expanding OECM in areas managed by the government.
What is the status of achievement in Japan?
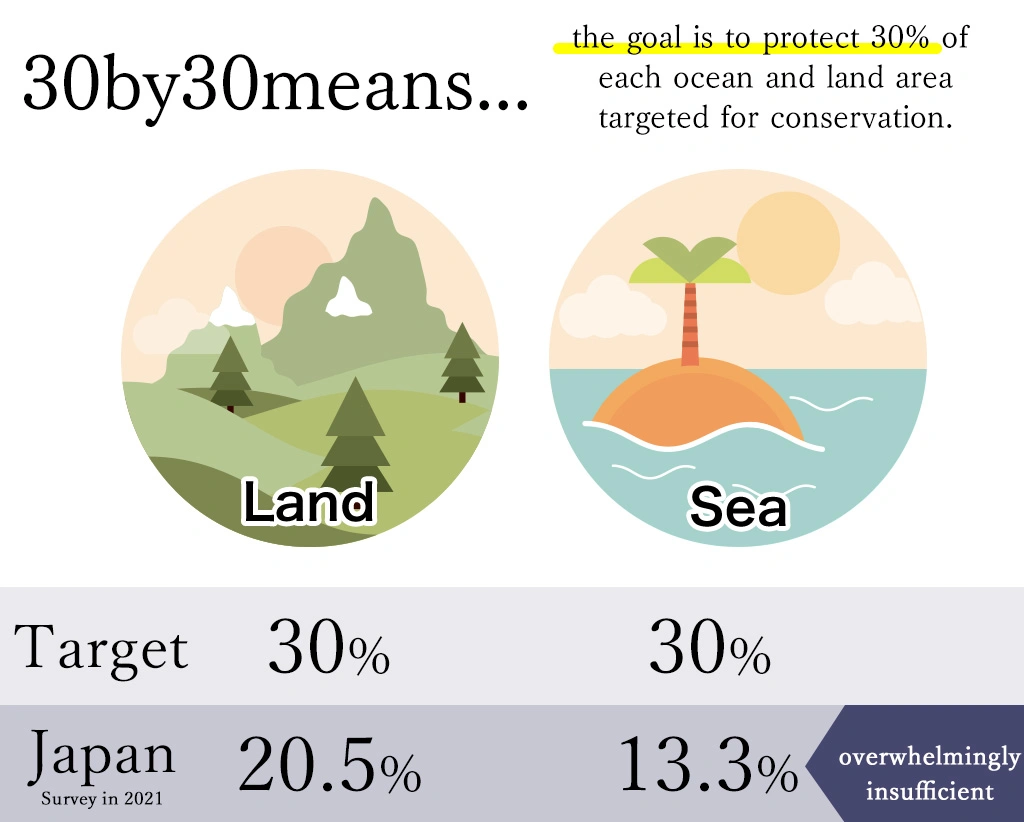
In fact, the 2021 survey shows that only 20.5% of the land and 13.3% of the sea are recognized as conservation areas, and that national parks and other areas managed by the government alone are overwhelmingly insufficient. It is not easy for the Japanese government to conserve 30% of the country’s land.
*1 30 by 30 Targets and the Global Situation
Japan Economic Research Institute
Feasibility study on OECM as a business x community strategy – Utilization of nature symbiosis sites and its challenges
What are “nature symbiosis sites” starting in Japan?
A natural symbiosis site is “an area where biodiversity is being conserved through the efforts of the private sector” and is recognized by the national government. In other words, it is a kind of private sector protected area.
When a landowner applies for a site and it passes the review by the Ministry of the Environment, the area other than those duplicated as a protected area will be registered as an OECM as well.
In other words, “nature symbiosis sites” are an initiative to increase the number of OECMs.
The main advantage of being certified as a symbiosis with nature site is that the company or organization that owns the site can publicize its biodiversity efforts to investors, consumers, and users, and can expect to increase its corporate value, which at present is mainly to strengthen its brand power.
However, the pros and cons of economic incentives are also being considered*2 for the future.
Examples of areas that may be certified as nature symbiosis sites
Corporate forests, National Trust, bird sanctuaries, biotopes, nature observation forests, satochi Satoyama, forest operation sites, water source forests, shrine and temple forests, areas with cultural and historical value, green areas on corporate premises, residential forests, green roads, green areas in cities, wind conservation forests, parks in cities, golf courses, ski resorts, research institutions of Forests, forests used for environmental education, forests for disaster prevention and mitigation, reservoirs, riverbeds, forests for water source recharge and carbon fixation and absorption, rooftops of buildings, grasslands for testing and training…etc.
*2
Status of Study on Economic Incentives, etc. for 30 by 30 (Ministry of the Environment)
https://www.env.go.jp/nature/30by30_00001.html
30 by 30 in which each of us can participate.
In other countries, OECM is promoted as a national initiative, and the private sector and municipality are not in a position to actively intervene.
Japan, on the other hand, has adopted the concept of “nature symbiosis sites,” which means that the national government, local communities, organizations, and companies are all cooperating in the conservation of 30% of the country’s land.
Isn’t it exciting to think that each of us can participate in this effort and become a member of the international conservation movement?
Nature Positive is hard to quantify and difficult to understand, so the only way to restore it is through partnership. If that is the case, the idea of a nature symbiosis site where various stakeholders can cooperate makes sense.
Japan is one of only 36 biodiversity hotspots in the world. Important nature and creatures are scattered throughout the Japanese archipelago. We must continue to protect them with the help of many people.
CLASS EARTH Corporation is participating in the “30 by 30 Alliance for Biodiversity” to contribute to the expansion of OECM and nature symbiosis sites.

▼Please read this as well.









